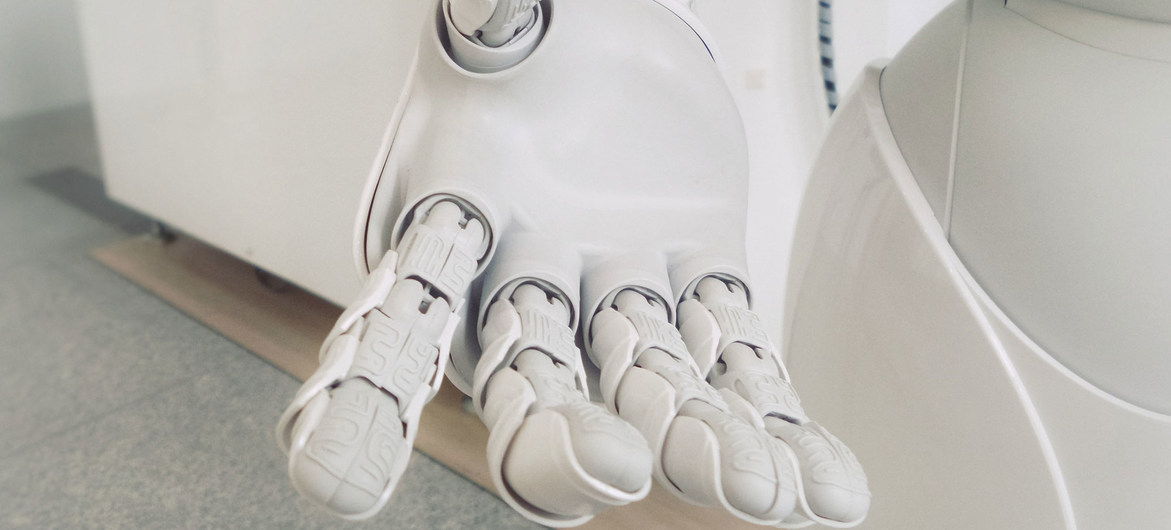
After double-digit growth in the sector in recent years, the Geneva-based World Intellectual Property Organization said that “assistive technologies” are increasingly finding their way into mass-market consumer applications.
The result offers the possibility of greater autonomy for users in negotiating their environment, work and home life.
Two billion people in need by 2030
“Currently, an estimate of one billion people around the world benefit from an assistive technology. That figure is expected to double by 2030 as the population ages,” said Marco Aleman, Assistant Director General, IP (Intellectual Property) and Innovations Ecosystem Sector.
In addition to improvements in established products, including wheelchair seats or wheels that can be adjusted for difficult terrain, environmental alarms and Braille-enabled devices, WIPO said that “emerging assistive” devices grew three times faster between 2013-2017, with a 17 per cent average annual growth rate.
Robot helpers
Products in this sector include assistive robots in the home and wearable products for visually impaired people and smart glasses according to the WIPO Technology Trends Report 2021: Assistive Technologies.
Other emerging products that are expected to catch on include advanced walking aids such as balancing aids and “smart” canes, advanced prosthetics – including neuroprosthetics, smart and 3D printed prosthetics – and wearable “exoskeleton suits” for the lower and upper body, to help with lifting chores and improve mobility.
“The assistive technology came from the military applications and now we see increasing applications in manufacturing and industry, so it helps people enhance their power, they can carry more weight, so that we already see,” noted Irene Kitsara, Industrial Property Information Officer, IP and Innovations Ecosystem Sector at WIPO.
Brainwaves
By 2030, the WIPO official maintained that “it will be a reality (to see) more advancements in (the) brain-to-machine interface…which allow us to control different devices: computers, mobile phones”.
Help is also much more widely available than previously for people with hearing difficulties, thanks to recent technology advances in “environment-controlling and mind-controlled hearing aids, with cochlear implants accounting for nearly half of patent filings.
The areas of greatest growth in hearing are in non-invasive bone conduction devices (31 per cent annual growth), WIPO said.
“Now we see over-the-head – the counter – hearing aids, which are (US health regulator) FDA-approved in the States, which is considered a consumer electronic good, but it can serve people who are not considered persons with a functional limitation as such but who would not otherwise benefit from a hearing aid,” said Irene Kitsara.
Smart transformation
The same transformation of conventional products into “smart” devices is also set to reach the personal health care sector, with innovations including “smart diapers and feeding assistant robots”, WIPO maintained.
“We can use the same applications for digital health and better health,” continued Kitsara. “As a result of that we can see more products, we can see increased competition, and something that was considered to be a niche area and a specialized product with very high prices, it starts going down.”
China, the US, Germany, Japan and the Republic of Korea are the five main origins of innovation in assistive technology, patent data filings show.
“When it comes to universities and public research centres, Chinese universities dominate the top,” said Aleman. “If we take the top 100 applicants among the 25 universities and research centres, 20 are Chinese, two American, one Korean, one from the Russian Federation and one from Japan.”