Ukrainians have increasingly woken up to the sound of suicide drones as Russia turns to Iranian-made imports to destroy civilian infrastructure in Ukraine. Now they may have another deadly Iranian weapon to worry about — ballistic missiles.
Cheap but effective, Shahed-136 and Shahed-131 “kamikaze” drones have already made a deadly impact in Ukraine.
If U.S. intelligence assessments pan out, Russia will soon be able to supplement its use of Iranian suicide drones and its own cruise and ballistic missiles with powerful short-range Iranian Fateh-110 and Zolfaghar ballistic missiles.
Coming as the Kremlin is reportedly struggling to maintain its depleted stockpile of aerial weapons as it ramps up strikes, the missiles would potentially boost Russia’s ability to continue its costly air campaign.
Jeremy Binnie, a Middle East defense specialist at the global intelligence company Janes, said having more missiles gives Russia “the ability to sustain the bombardment against Ukraine.”
Going Ballistic
The Fateh-110, which was unveiled in 2001 and has a stated range of 300 to 500 kilometers, was developed from a heavy artillery rocket dating from the 1980s. To increase the weapon’s accuracy, the Fateh-110 was given a guidance system and movable fins that allow it to be steered as it approaches its target.
The Zolfaghar, which debuted in 2016 and also has guidance capabilities, comes from the same family as the Fateh-110 but boasts a much longer range due to its use of a lighter carbon-fiber airframe and a smaller warhead.
Binnie said the Zolfaghar’s use against the Islamic State (IS) extremist group in eastern Syria confirmed that the missile was capable of reaching at least 650 kilometers, which he said is “a statement of how much the Iranian tactical missile program has really advanced over the years.”
Iran’s claim that the Zolfaghar can travel even farther — up to 700 kilometers — would put the western Ukrainian city of Lviv within range of strikes launched from Russian territory, while the more powerful Fateh-110 could potentially hit the city from Belarus, which has served as a staging ground for Russian attacks.
While there has been no indication that Russia plans to purchase launching systems from Iran, Binnie suggests that the Russian military could pair the missiles with existing equipment because the Iranian launchers were adapted from a Soviet-era system.
“It might be possible for the Russians to quickly adapt some old equipment they have lying around into launch systems,” Binnie said.
The Iranian military, he added, fitted the Soviet system to trucks, allowing for mobility and concealment.
“Those civilian trucks can be covered over to make it hard to spot that they’re actually missile launchers,” Binnie said.
‘Lawnmowers’ And ‘Mopeds’
Iranian military drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have been homing in on targets across Ukraine for months.
The buzzing sound of the Iranian Shahed-136 and Shahed-131 drones, built with off-the-shelf components, have earned them derisive monikers such as “lawnmowers” and “mopeds.” But the slow-moving, low-flying drones, which are maneuvered to crash into their target, have proven themselves capable of hitting their mark both in terms of military effectiveness and cost.

“It is capable of extracting or delivering attrition and damage when launched, but it costs little compared to other UAVs that Russia has in its own arsenal,” said Samuel Bendett of the Virginia-based Center for Naval Analyses (CNA).
Ukraine alleges Russia has ordered 2,400 of the Iranian suicide drones, and its military has claimed to have shot them down in great numbers, often using conventional anti-aircraft guns or even small-arms fire. But their ability to be launched in bunches of five — often from the cover of civilian trucks — improves their chances of reaching their target.
“The Ukrainians are stopping most of these, but the whole point of these drones is that they fly in a large mass,” Bendett said. “The air defense does not always catch all of them. All it takes is for several or even one to make it through.”

The estimated range of the Shahed-136 varies, but Iran says it is capable of traveling 2,500 kilometers. The slightly smaller and older Shahed-131, which has been used by Huthi rebels in Yemen to attack Saudi targets in the Arabian Peninsula, has been estimated to have a range of 900 kilometers, according to tests conducted by the Ukrainian military.
Ukraine’s Defense Ministry has published multiple images of downed Shahed-136 drones in recent weeks, and the Ukrainian National Guard on October 19 claimed to have shot down a Shahed-131.
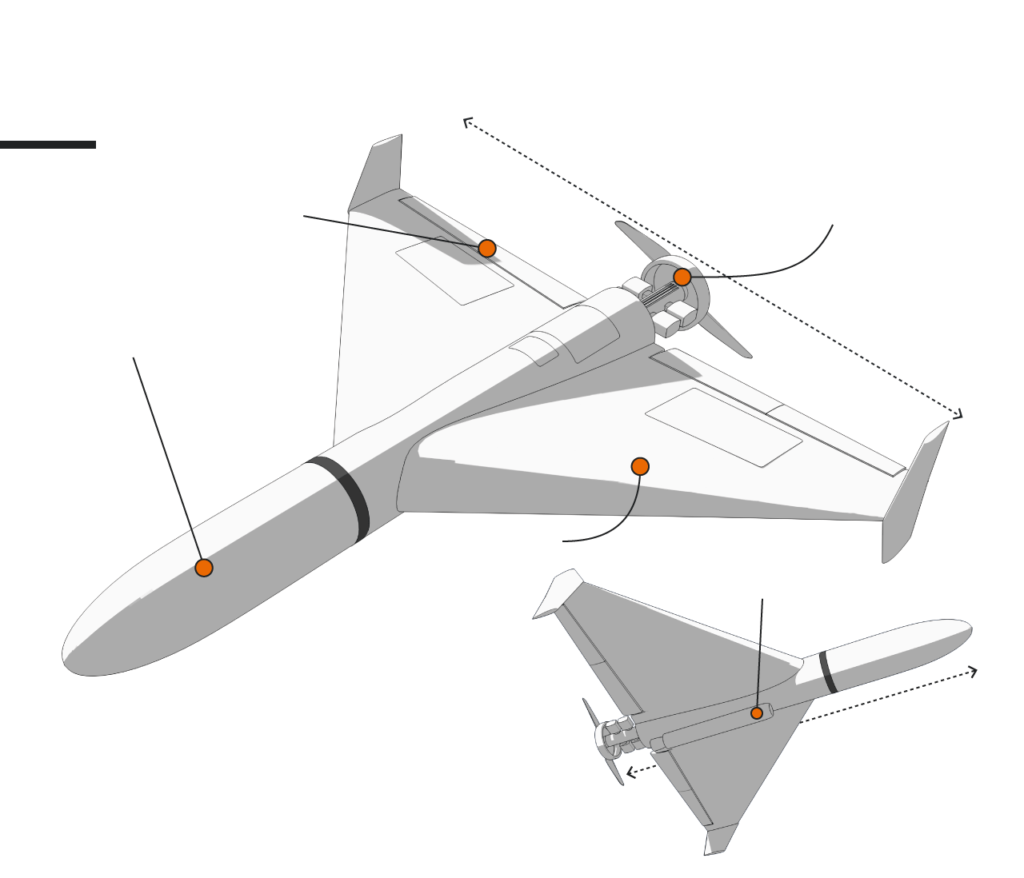
Ukraine has also claimed to have shot down a more advanced Iranian combat UAV, the Mojer-6 drone capable of carrying out both reconnaissance missions and aerial strikes within a range of 200 kilometers. There have also been reports of Russian interest in obtaining Iran’s Shahed-129 and Shahed-191 combat drones.
“When launched from any territory that Russia controls or is allied with — anywhere from the south, from the Donbas, from Belarus — they’re able to strike a lot of Ukrainian targets,” Bendett said.
In addition to the U.S. intelligence assessment that Russia will soon boost its arsenal with Iranian ballistic missiles, as first reported by The Washington Post on October 16, the White House on October 20 said that Iranians are now “directly engaged on the ground” in Moscow’s war against Ukraine after sending “a relatively small number” of personnel from the Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps to assist Russian forces in using the Iranian drones.
Iran has denied sending combat drones to Russia, and Moscow has rejected claims that it is using Iranian UAVs.
Images of downed Iranian drones appear to show that they have been rebranded to look Russian-made, experts say, with the markings in Cyrillic naming them as the Geran-1 (the Shahed-131) and Geran-2 (the Shahed-136).

Observers are widely skeptical of Russia’s denials, noting that the drones are essentially identical right down to the font of the serial numbers. Even Russian Defense Ministry experts have unwittingly admitted that the suicide drones are Iranian.
But the rebranding of the drones to make them appear to be Russian has opened the possibility that Moscow could, if it is not already doing so, seek to manufacture or assemble the Iranian drones on its own territory.
Sustaining A Campaign
The new aerial weaponry fits well with the Russian military’s renewed focus on striking military and civilian targets far from the front lines in southern and eastern Ukraine. The air assault has ratcheted up following the October 8 appointment of Colonel General Sergei Surovikin, a former Aerospace Forces commander, to lead the Russian war effort.
Just days after Surovikin’s appointment, Russia launched the biggest air strikes since the beginning of its invasion of Ukraine in February. Moscow said the drone and missile strikes, which targeted civilian areas and infrastructure in cities throughout Ukraine, were in response to a bomb blast that damaged a key bridge linking Russia to the occupied Crimean Peninsula.
While the Kremlin has accused Ukraine’s intelligence services of carrying out the “terrorist” attack on the Crimea Bridge, Ukraine has denied responsibility.
Since the initial air assault in response to the bridge blast, Russia has continued to pound Ukrainian infrastructure, often targeting power plants in what Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy has said is a deliberate effort to wear down the Ukrainian people by denying them heat and electricity as winter approaches.
“Civilian infrastructure is obviously the new layer in this war. The Ukrainian economy is now the target, the Ukrainian population is now the target,” Bendett said.
Hard To Stop
The hypersonic speed and high trajectory of Iran’s Fateh-110s and Zolfaghars, should they arrive, would be extremely difficult for Kyiv to counter without a network of high-tech and costly antimissile batteries it currently does not possess.
Ukraine has repeatedly requested more advanced missile-defense systems from the West, and in the face of the threat of the delivery of Iranian ballistic missiles reportedly sent an official request to Israel this week for components of its “Iron Dome” system.
While the United States has said that it is seeking to expedite the process of sending two U.S. air defense systems known as NASAMS, Washington has appeared reluctant to provide more advanced Patriot missile systems.
Janes’ defense expert Binnie is skeptical that the delivery of the Patriot system, which has proven to be successful in shooting down ballistic missiles, is realistic for Ukraine.
“It’s eye wateringly expensive and it’s probably not really practical because each [missile] battery only covers one city,” he said. “You would never get enough batteries to get the coverage you would want. You just wouldn’t be able to find them, produce them, and train enough Ukrainians.”