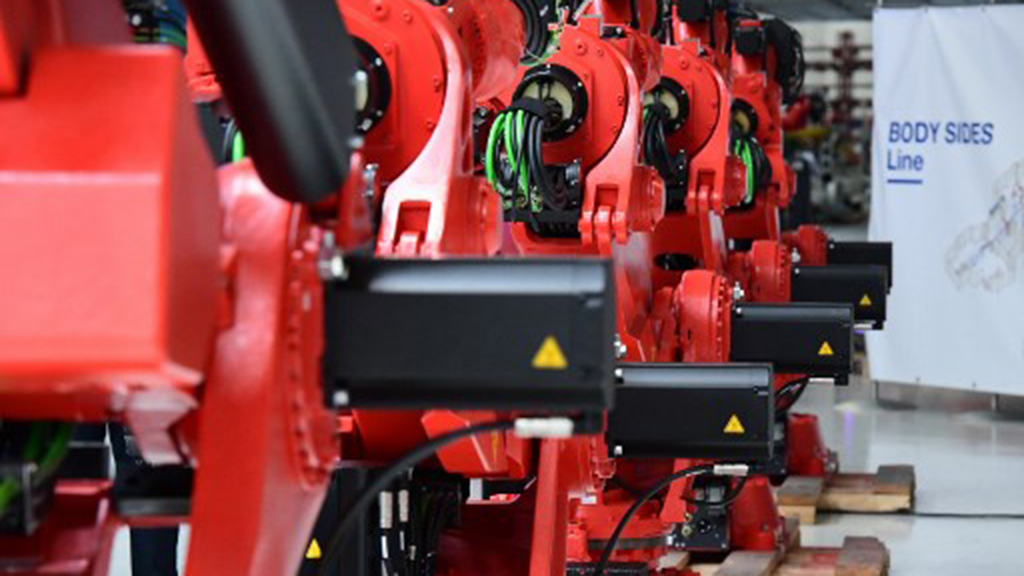
European enterprises have been hit hard by the Covid-19 pandemic, as many have had to shut or reduce their workforce while finding new ways to work within new restrictive measures. Before making the necessary digital and green transitions, industry in the EU needs to recover from the pandemic.
During the November plenary, MEPs are set to reiterate their call for the European Commission to revise its March 2020 proposal on the EU’s new industrial strategy. In a draft report adopted on 16 October, the members of the industry, research and energy committee demanded a shift in the EU approach to industrial policy in the wake of the pandemic by helping businesses cope with the crisis and face the digital and environmental transitions.
How the Parliament foresees the EU’s industry landscape
Industry represents more than 20% of the EU’s economy and employs about 35 million people, with many millions more jobs linked to it at home and abroad. In addition it accounts for 80% of goods exports. The EU is also a top global provider and destination for foreign direct investment.
In the context of the new industrial strategy, the EU should enable companies to contribute to its climate-neutrality targets – as outlined in the Green Deal roadmap – support firms, particularly small and medium enterprises in the transition to a digital and carbon-neutral economy and help create high-quality jobs, without undermining the EU’s competitiveness.
According to MEPs; such a strategy should consist orf two phases: a recovery phase to consolidate jobs, reactivate production and adapt to a post-Covid period; followed by reconstruction and industrial transformation.
Empowering smaller firms to achieve sustainable growth
Small and medium-sized enterprises are the backbone of the EU economy, accounting for more than 99% of all European business. The industrial strategy should focus on them, as many have contracted debts due to national coronarivus measures, reducing their investment capacity, which is likely to trigger sluggish growth in the long-term.
Helping industry recover from the socio-economic crisis
The Covid Recovery Fund is part of the first phase in responding to the emergency and should be distributed according to the level of damage suffered, challenges faced and amount of financial support already received through national aid schemes.
Preference should be given to companies and smaller firms oriented towards the digital and environmental transformation and thus investing in environmentally sustainable activities.
MEPs want to:
- Ensure that the green and digital transitions are fair and socially just and are followed by initiatives to train workers
- Create a new impact assessment of the potential costs and burdens of the transition for European companies, including small and medium-sized enterprises
- Make sure that state aid provided in the emergency phase does not lead to permanent distortions in the single market.
- Bring strategic industries back to the EU
Investing in greener, digital and innovative enterprises
During the second phase, the industrial strategy should ensure competitiveness, resilience and long-term sustainability. Goals include:
- Focussing on the social aspects of the structural change
- Revitalising territories that rely on fossil fuels using the Just Transition Fund, which is part of the EU’s climate finance plan
- Ensuring EU subsidies go to environmentally sustainable companies and enhancing sustainable financing to companies in the decarbonisation process
- Using the Border Carbon Adjustments mechanism to help protect EU manufacturers and jobs from unfair international competition
- Having a research-based pharmaceutical industry and a medicine shortage risk mitigation plan
- Exploiting the circular economy, privileging the “energy efficiency first” principle, energy savings and renewable energy technologies
- Using gas to transition away from fossil fuels and hydrogen as a potential breakthrough technology
- Investing in artificial intelligence and implementing a single European digital and data market, building a better digital taxation system and developing European standards on cybersecurity
- Investing more in research and development
- Revising EU antitrust rules to ensure global competitiveness